Table Of Content

Enter your experimental design variable names (factors) and values (levels). Examples of levels are ‘red’ and ‘blue’ for ‘color’; 10, 20, 30 for ‘size’; ‘square’ and ‘round’ for 'shape'. The other type of hypothesis—which is a major advantage of the approach—involves the assessment of interaction effects. These are observed when the effect of a factor is dependent on the level of the other factors in the experimental model. The difference concerns what happens to the sample size requirements if we decide we want to add an experimental condition to an RCT versus what happens if we decide we want to add a factor to a factorial experiment.
Minitab DOE Example
For most scenarios, however, near-optimal designs are adequate and not hard to obtain. Simultaneous examination of multiple factors at two levels can reveal which have an effect. Factorial designs are the basis for another important principle besides blocking - examining several factors simultaneously. We will start by looking at just two factors and then generalize to more than two factors. Investigating multiple factors in the same design automatically gives us replication for each of the factors. As seen above, RPM is shown with a positive effect for number of theoretical stages, but a negative effect for wt% methanol in biodiesel.
Optimal experimental design for precise parameter estimation in competitive cross-reaction equilibria

For example, people are either low in hypochondriasis or high in hypochondriasis; they cannot be tested in both of these conditions. Second, such studies are generally considered to be experiments as long as at least one independent variable is manipulated, regardless of how many non-manipulated independent variables are included. Third, it is important to remember that causal conclusions can only be drawn about the manipulated independent variable. For example, Schnall and her colleagues were justified in concluding that disgust affected the harshness of their participants’ moral judgments because they manipulated that variable and randomly assigned participants to the clean or messy room. But they would not have been justified in concluding that participants’ private body consciousness affected the harshness of their participants’ moral judgments because they did not manipulate that variable. It could be, for example, that having a strict moral code and a heightened awareness of one’s body are both caused by some third variable (e.g., neuroticism).
Table of Contents
A new multi-factor multi-objective strategy based on a factorial presence-absence design to determine polymer additive ... - ScienceDirect.com
A new multi-factor multi-objective strategy based on a factorial presence-absence design to determine polymer additive ....
Posted: Tue, 18 Oct 2022 02:33:51 GMT [source]
For example, the individuals randomly assigned to Condition 2 would receive a home visit, but neither of the other two intervention components. Those randomly assigned to Condition 7 would receive the keeping a food diary and increasing physical activity components, but would not receive a home visit. In addition to looking at the employment sector, the researchers also look at gender. In this example, the employment sector and gender of the graduates are the independent variables, and the starting salaries are the dependent variables.
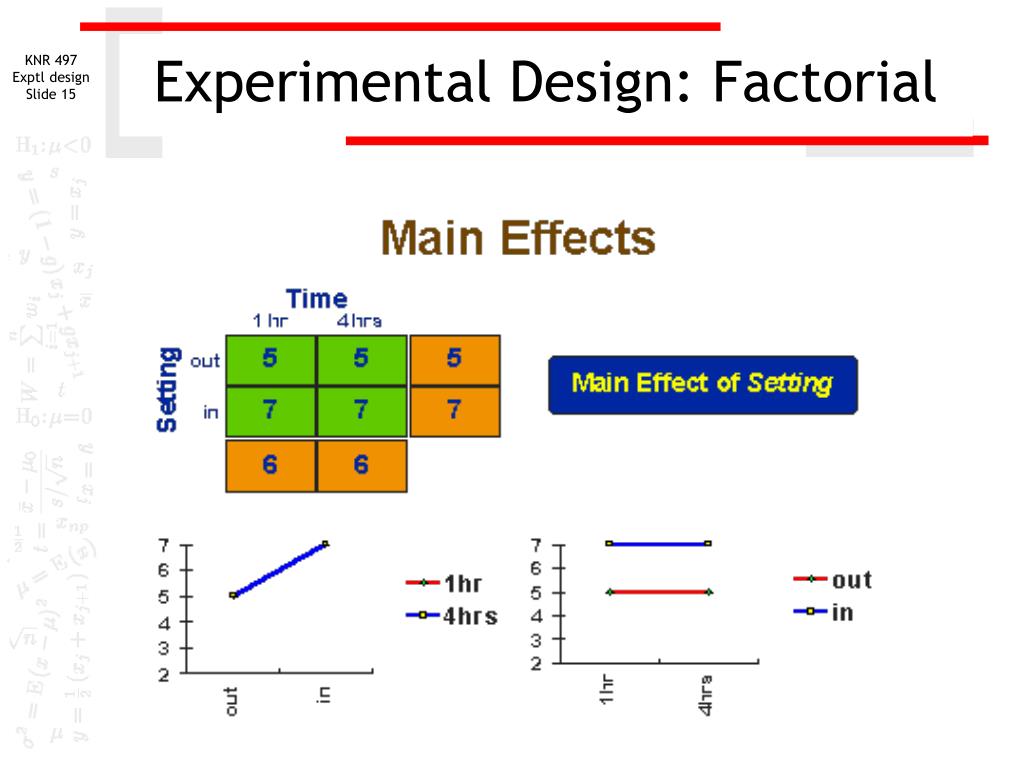
This is what was seen graphically, since the graph with dosage on the horizontal axis has a slope with larger magnitude than the graph with age on the horizontal axis. In the previous section, we looked at a qualitative approach to determining the effects of different factors using factorial design. Now we are going to shift gears and look at factorial design in a quantitative approach in order to determine how much influence the factors in an experiment have on the outcome. Experiments that include more than one independent variable in which each level of one independent variable is combined with each level of the others to produce all possible combinations.
A full factorial design, also known as fully crossed design, refers to an experimental design that consists of two or more factors, with each factor having multiple discrete possible values or “levels”. In unconstrained settings where a classical design would be appropriate, optimal designs often turn out to be the same as their traditional counterparts. Or, for a design with a sample size of 24, three factors, no blocks, and an assumed model that includes the three factor effects and all of the two-factor interactions, both the D- and I-criteria yield as optimal the two-level full-factorial design with three replicates. Factorial Analysis is an experimental design that applies Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) statistical procedures to examine a change in a dependent variable due to more than one independent variable, also known as factors.
1: Factorial Designs
In the figure, the area selected in black is where the responses will be inputted. For instance, if the purity, yield, and residual amount of catalyst was measured in the DOE study, the values of these for each trial would be entered in the columns. The default factors are named "A", "B", "C", and "D" and have respective high and low levels of 1 and -1. The name of the factors can be changed by simply clicking in the box and typing a new name. Additionally, the low and high levels for each factor can be modified in this menu. Since the high and low levels for each factor may not be known when the design is first created, it is convenient to be able to define them later.
Implementing Clinical Research Using Factorial Designs: A Primer
In the "Modify Design" menu, users can modify factors, replicate design, randomize design, renumber design, fold design, and add axial points. To change the factors, click the "Modify factors" radio button and then "Specify" to see the following options menu. Ignoring the first row, look in the last stage and find the variable that has the largest relative number, then that row indicates the MAIN TOTAL EFFECT.
The Pareto charts are bar charts which allow users to easily see which factors have significant effects. Analysis was performed on the DOE study to determine the effects of each factor on the responses. Only first order terms were included in the analysis to create a linear model. Pareto charts for both wt% MeOH in biodiesel and number of theoretical stages are shown below. Because experiments from the POD are time consuming, a half fraction design of 8 trial was used. Factors A - D can be renamed to represent the actual factors of the system.
While more research on IC interactions is surely needed, our research has consistently found such interactions (Cook et al., 2016; Fraser et al., 2014; Piper et al., 2016; Schlam et al., 2016). Thus, it might be difficult in many cases to assume conditions that would justify the use of a fractional factorial design. If one of the independent variables had a third level (e.g., using a handheld cell phone, using a hands-free cell phone, and not using a cell phone), then it would be a 3 × 2 factorial design, and there would be six distinct conditions. Notice that the number of possible conditions is the product of the numbers of levels. A 2 × 2 factorial design has four conditions, a 3 × 2 factorial design has six conditions, a 4 × 5 factorial design would have 20 conditions, and so on.
Optimization of thiamethoxam adsorption parameters using multi-walled carbon nanotubes by means of fractional ... - ScienceDirect.com
Optimization of thiamethoxam adsorption parameters using multi-walled carbon nanotubes by means of fractional ....
Posted: Tue, 23 Jun 2020 11:36:55 GMT [source]
From this one can see that there is an interaction effect since the lines cross. One cannot discuss the results without speaking about both the type of fertilizer and the amount of water used. Using fertilizer A and 500 mL of water resulted in the largest plant, while fertilizer A and 350 mL gave the smallest plant. Fertilizer B and 350 mL gave the second largest plant, and fertilizer B and 500 mL gave the second smallest plant.
These runs are chosen carefully so that under the reasonable assumptions of effect sparsity and hierarchy, the terms of interest (e.g., main effects and two-factor interactions) can be estimated. Once the factorial effects have been computed, the natural question is whether they are large enough to be of statistical and scientific interest. Thus, if all factorial terms are included in the model, traditional regression-based inferences cannot be made because there is no estimate of residual error. In a three-factor experiment, this issue can be addressed by replication, but for larger studies this might be infeasible owing to the large number of treatments. Alternatively, an investigator might modify an intervention when it co-occurs with a particular, second intervention component. For instance, assume that a design has three factors; two are medication factors (e.g., varenicline, on/off, in one factor and NRT product [nicotine patch vs. nicotine lozenge], in a second factor).
A positive effect means that as RPM increases, the number of theoretical stages increases. Whereas a negative effect indicates that as RPM increases, the wt% methanol in biodiesel decreases. When choosing operating conditions for the POD, RPM should be maximized to minimize the residual methanol in biodiesel and maximize the number of theoretical stages achieved.
If she were only to perform the experiment using these variables–the sleep deprivation being the independent variable and the performance on the driving test being the dependent variable–it would be an example of a simple experiment. Let’s name our factors A, B and C, and use –1 and +1 for the low and high levels, respectively (Table 1). Even though there is no replication, this 23 full factorial design can detect factor effects, if some sensible assumptions are made. In addition, SuperGym offers 4 different workout plans, A through D, none of which are directly catered to any of the different types. Create an experimental factorial design that could be used to test the effects of the different workout plans on the different types of people at the gym.
The Main Total Effect can be related to input variables by moving along the row and looking at the first column. To get a mean factorial effect, the totals needs to be divided by 2 times the number of replicates, where a replicate is a repeated experiment. When there is a large interaction, main effects have little practical meaning as a significant interaction often masks the significance of main effects. The last four column vectors belong to the A × B interaction, as their entries depend on the values of both factors, and as all four columns are orthogonal to the columns for A and B. Time series analysis is used to analyze data collected over time in order to identify trends, patterns, or changes in the data.
The lesson here, therefore, is to spend more time sleeping and studying, and less time with your boyfriend or girlfriend. However, the Normal Plot displays whether the effect of the factor is positive or negative on the response. Minitab 15 Statistical Software is a powerful statistics program capable of performing regressions, ANOVA, control charts, DOE, and much more.

No comments:
Post a Comment